XPS
SPECIALIST XPS TECHNIQUES
X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a powerful analytical technique that’s utilised throughout materials science. Primarily, it is used to determine the elemental composition and chemical state of a material’s surface. This technique is also known as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (PES) and is grounded in the photoelectric effect. This is where electrons are ejected from a material’s surface upon exposure to x-ray radiation. The kinetic energy of these emitted electrons is measured to reveal detailed information about the surface.
PRECISE INSIGHTS ACROSS SECTORS
How XPS Works
XPS operates under ultra-high vacuum conditions to prevent interference from atmospheric gases and contaminants, which can skew results. By analysing the binding energies of photoelectrons emitted from the surface of a material, XPS provides insights into both the elemental composition and the chemical states of the elements present. This makes it an invaluable tool for studying thin films, coatings, and other surface-sensitive applications.
You can find out more about the applications of our Ion Beams for XPS by visiting our applications page.
CUTTING-EDGE TECHNOLOGY
Near-Ambient-Pressure XPS (NAP-XPS)
Traditionally, XPS requires a high-vacuum environment to function accurately. However, recent advancements have led to the development of Near-Ambient-Pressure XPS (NAP-XPS). This cutting-edge technology enables the analysis of surfaces under conditions that more closely mimic real-world environments, such as in the presence of gases and liquids.
NAP-XPS opens up new possibilities for studying surface reactions, catalysis, and corrosion processes in conditions that are more representative of practical applications.
To learn about the impact of NAP-XPS in real-life scenarios, please read a research publication.

A RANGE OF SOLUTIONS
Ion Beams for XPS Analysis
One of the challenges in XPS analysis is maintaining an uncontaminated surface. Even minor surface contaminants can affect the accuracy of the results. To address this, Ion Beams are used to clean the surface before analysis. Ion Beams can effectively remove contaminants and prepare the surface, ensuring that the data obtained is both accurate and reliable.
Types of Ion Beams:
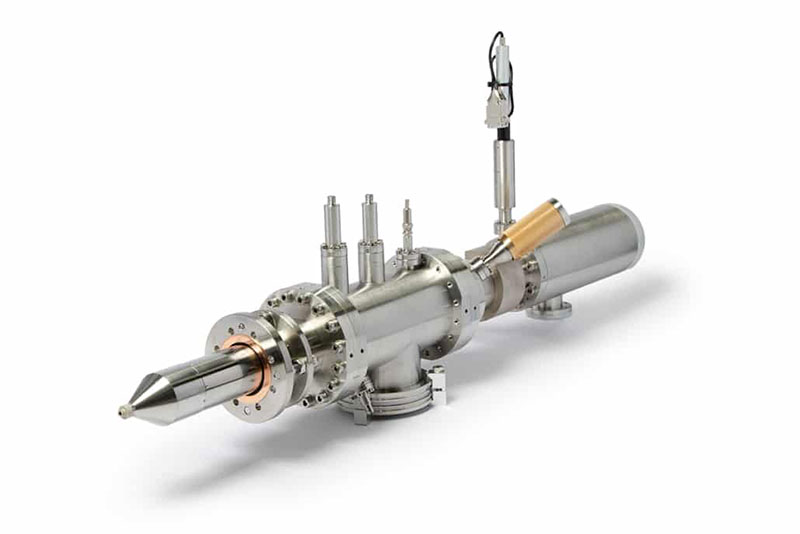

These are commonly used in XPS for surface cleaning and depth profiling. C60 clusters are particularly effective for sputtering large areas and providing uniform depth profiles, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.